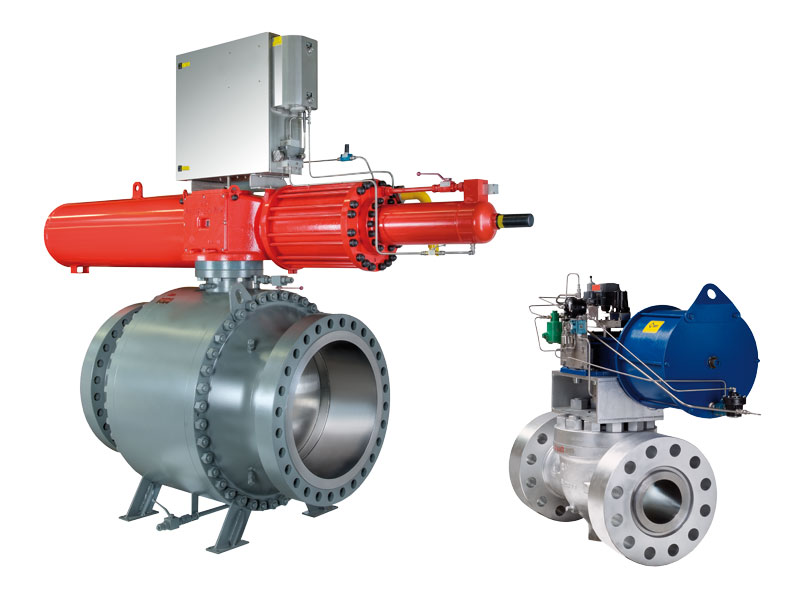
A ball valve (BV) is a quarter turn valve used for changing the direction of a process stream (divert or shut off). Ball valves can be automated to automatically shutdown or open depending on the orientation of the actuator. True ball valves should not be used as control valves as velocities between the ball and seat can be high enough to wash out the sealing portion of the valve. The ball on the valve can be characterized to act as a control valve such as a V-ball type design.
Since the ball valve is a quarter turn valve, it is very easy to automate.In large applications, a ball valve may be economically prohibitive. This is due to the amount of metal that makes up the body and ball. For large diameter applications that require a quarter turn valve, a butterfly valve may be appropriate.
The bore of a ball valve is the area through which the fluid flows. A full bore valve has an opening that is equal to the nominal pipe size (NPS) of the flowing pipe. A standard bore ball valve typically has an area that is equal to the NPS of the pipe one size smaller than the flowing line.
Full bore ball valves are the ideal solution where pressure drop is a concern. Full bore valves are the ideal choice where pigging of process lines is a major consideration. Normal “dumb” pigs may be able to deform across a reduced bore ball valve. Smart pigs, however cannot. Full port valves are normally used when inserting sample probes, injection quills or interface probes to facilitate removing the device from the system while under full line pressure.
Trunnion Design is simply the use of upper and lower supports to retain the ball under pressure. Named for the “trunnion” historically used to support a cannon, a ball valve trunnion essentially doubles the safety and usability of a ball valve. Another important benefit of the trunnion design is that it allows the Ball Valve to act as a true union: The downstream piping can be disconnected under full upstream pressure (user is responsible to ensure that downstream piping is drained of liquid and that valve is indeed closed and secured to upstream piping).
The trunnion on a two-way ball valve supports the ball in much the same way as the stem does at the top. The trunnion on a three-way ball valve is a much different design, being more like a supporting ring, but provides the exact same function and inherent stability.
Floating ball valves are used in low pressure or small bore processes. A floating ball valve has two seats, located upstream and downstream of the ball. When the valve is closed, differential pressure across the valve assists in seating the ball. The adjacent ball valve is a ANSI 300 8″ soft seated floating ball valve with manual actuator (handwheel).
Metal Seated Ball Valves are described as extreme service valves. They are called metal seated ball valves because the ball and the seat are made out of metal. These are typically seen in high pressure & high temperature applications such as steam in a power generation plant. Metal Seated valves are high torque valves due to the high pressure differential across the valve and the metal ball and seat.
In order to completely seal, the seat must be machined to exactly match the ball. If there is any misalignment of the ball, the valve will leak. This is because the metal seat is less forgiving and less pliable than soft seated valves.
We in ITOK TEJERAT ARMAN are able to offer you variety of ball valves in different material, rating and operation method (handle, bevel gear, electric, pneumatic, etc.), to answer all your industrial needs.
- API Standards:
API Spec 6D, API Std 598. - ASME Standards:
API Spec 6D, API Std 598. - BSI Standards:
BS 2080, BS 5159 , BS 5351 . - MSS Standards:
MSS-SP-61, MSS-SP-72, MSS-SP-84.